Install John The Ripper Password Cracker Versi Komunitas di Linux Software John The Ripper biasanya digunakan untuk memecahkan linux y windows. Tutorial John The Ripper Kita akan menggunakan cara kuno untuk mendapatkan password root dan seluruh password user yang ada di sebuah shell, disini penulis menggunakan.
- Aug 13, 2015 How to Install 'John the Ripper' On Linux – A Free Password Cracker Tool August 13, 2015 by saurav.roy Security of your important data is the most crucial concern, John the Ripper is a free tool widely used by ethical hackers and security testers to check and crack passwords.
- John The Ripper (JTR) adalah suatu sortware untuk mengcrack password yang cepat yang tersedia pada banyak platfom, antara lain UNIX, Windows, DOS, BeOS dan OpenVMS. Tujuan utama dari John The Ripper adalah untuk mendeteksi kelemahan password pada sistem UNIX (termasuk Linux).
- Installing John the Ripper. First of all, most likely you do not need to install John the Ripper system-wide. Instead, after you extract the distribution archive and possibly compile the source code (see below), you may simply enter the 'run' directory and invoke John from there.
John the Ripper is a fast password cracker. Its primary purpose is todetect weak Unix passwords. Besides several crypt(3) password hash types,supported out of the box include fast built-in implementations of SHA-cryptand SunMD5, Windows NTLM (MD4-based) password hashes, various macOS andMac OS X user password hashes, fast hashes such as raw MD5, SHA-1, SHA-256,and SHA-512, various SQL and LDAP server password hashes, as well as manynon-hashes such as SSH private keys, S/Key skeykeys files, Kerberos TGTs,encrypted filesystems such as macOS .dmg files and 'sparse bundles',encrypted archives such as ZIP, RAR, and 7z, encrypted document files suchas PDF and Microsoft Office's - and these are just some examples.
Read more at:
How to purchase microsoft word. This version integrates lots of contributed patches, including GPU support,dynamic expressions, has fallback for CPU SIMD extensions and for OMP,moreover, has on device mask acceleration and prince mode available.
John The Ripper Free Download
Its primary purpose is to detect weak Unix passwords. Besides several crypt(3) password hash types most commonly found on various Unix systems, supported out of the box are Windows LM hashes, plus lots of other hashes and ciphers in the community-enhanced version.
John the Ripper is free and Open Source software, distributed primarily in source code form. Launchey 1 1 9 download free. If you would rather use a commercial product tailored for your specific operating system, please consider John the Ripper Pro, which is distributed primarily in the form of 'native' packages for the target operating systems and in general is meant to be easier to install and use while delivering optimal performance.
What's New:
We've just released John the Ripper 1.9.0-jumbo-1, available from the usual place, here.
Only the source code tarball (and indeed repository link) is published right now. I expect to add some binary builds later (perhaps Win64). Game of thrones font mac.
It's been 4.5 years and 6000+ jumbo tree commits (not counting JtR core tree commits, nor merge commits) since we released 1.8.0-jumbo-1:
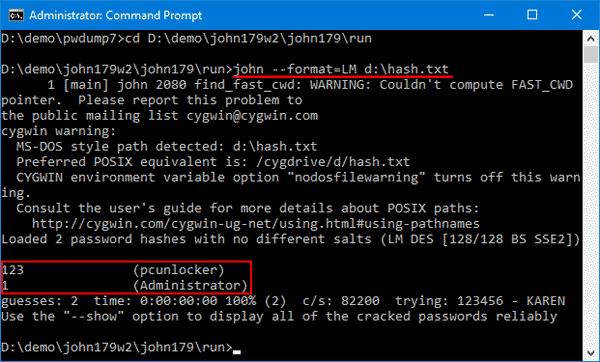
Cara Install John The Ripper Di Windows 10 Download
https://www.openwall.com/lists/announce/2014/12/18/1
During this time, we recommended most users to use bleeding-jumbo, our development tree, which worked reasonably well - yet we also see value
in making occasional releases. So here goes.
Top contributors who made 10+ commits each since 1.8.0-jumbo-1:
- magnum (2623)
- JimF (1545)
- Dhiru Kholia (532)
- Claudio Andre (318)
- Sayantan Datta (266)
- Frank Dittrich (248)
- Zhang Lei (108)
- Kai Zhao (84)
- Solar (75)
- Apingis (58)
- Fist0urs (30)
- Elena Ago (15)
- Aleksey Cherepanov (10)
About 70 others have also directly contributed (with 1 to 6 commits each), see doc/CREDITS-jumbo and doc/CHANGES-jumbo (auto-generated from git). Many others have contributed indirectly (not through git).
Indeed, the number of commits doesn't accurately reflect the value of contributions, but the overall picture is clear. In fact, we have the exact same top 6 contributors (by commit count) that we did for the 1.7.9-jumbo-8 to 1.8.0-jumbo-1 period years ago. That's some stability in our developer community. And we also have many new and occasional contributors. That's quite some community life around the project.
Unlike for 1.8.0-jumbo-1, which we just released as-is without a detailed list of changes (unfortunately!), this time we went for the trouble to compile a fairly detailed list - albeit not going for per-format change detail, with few exceptions, as that would have taken forever to write (and for you to read!) This took us (mostly magnum and me, with substantial help from Claudio) a few days to compile, so we hope some of you find this useful. Included below is 1.9.0-jumbo-1/doc/NEWS, verbatim.
Apple magic keyboard windows. Does das mechanical keyboard for mac have expose funtion key. Major changes from 1.8.0-jumbo-1 (December 2014) to 1.9.0-jumbo-1 (May 2019):
- Updated to 1.9.0 core, which brought the following relevant major changes:
- Optimizations for faster handling of large password hash files (such as with tens or hundreds million hashes), including loading, cracking, and '--show'. These include avoidance of unnecessary parsing (some of which creeped into the loader in prior jumbo versions), use of larger hash tables, optional use of SSE prefetch instructions on groups of many hash table lookups instead of doing the lookups one by one, and data layout changes to improve locality of reference. [Solar; 2015-2017]
- Benchmark using all-different candidate passwords of length 7 by default (except for a few formats where the length is different - e.g., WPA's is 8 as that's the shortest valid), which resembles actual cracking and hashcat benchmarks closer. [Solar, magnum; 2019]
- Bitslice DES implementation supporting more SIMD instruction sets than before (in addition to our prior support of MMX through AVX and XOP on x86(-64), NEON on 32-bit ARM, and AltiVec on POWER):
- On x86(-64): AVX2, AVX-512 (including for second generation Xeon Phi), and MIC (for first generation Xeon Phi).
- On Aarch64: Advanced SIMD (ASIMD). [Solar, magnum; 2015-2019]
- Bitslice DES S-box expressions using AVX-512's 'ternary logic' (actually, 3-input LUT) instructions (the _mm512_ternarylogic_epi32() intrinsic). [DeepLearningJohnDoe, Roman Rusakov, Solar; 2015, 2019] (In jumbo, we now also use those expressions in OpenCL on NVIDIA Maxwell and above - in fact, that was their initial target, for which they were implemented in both JtR jumbo and hashcat earlier than the reuse of these expressions on AVX-512.)
